What is a microtome for?
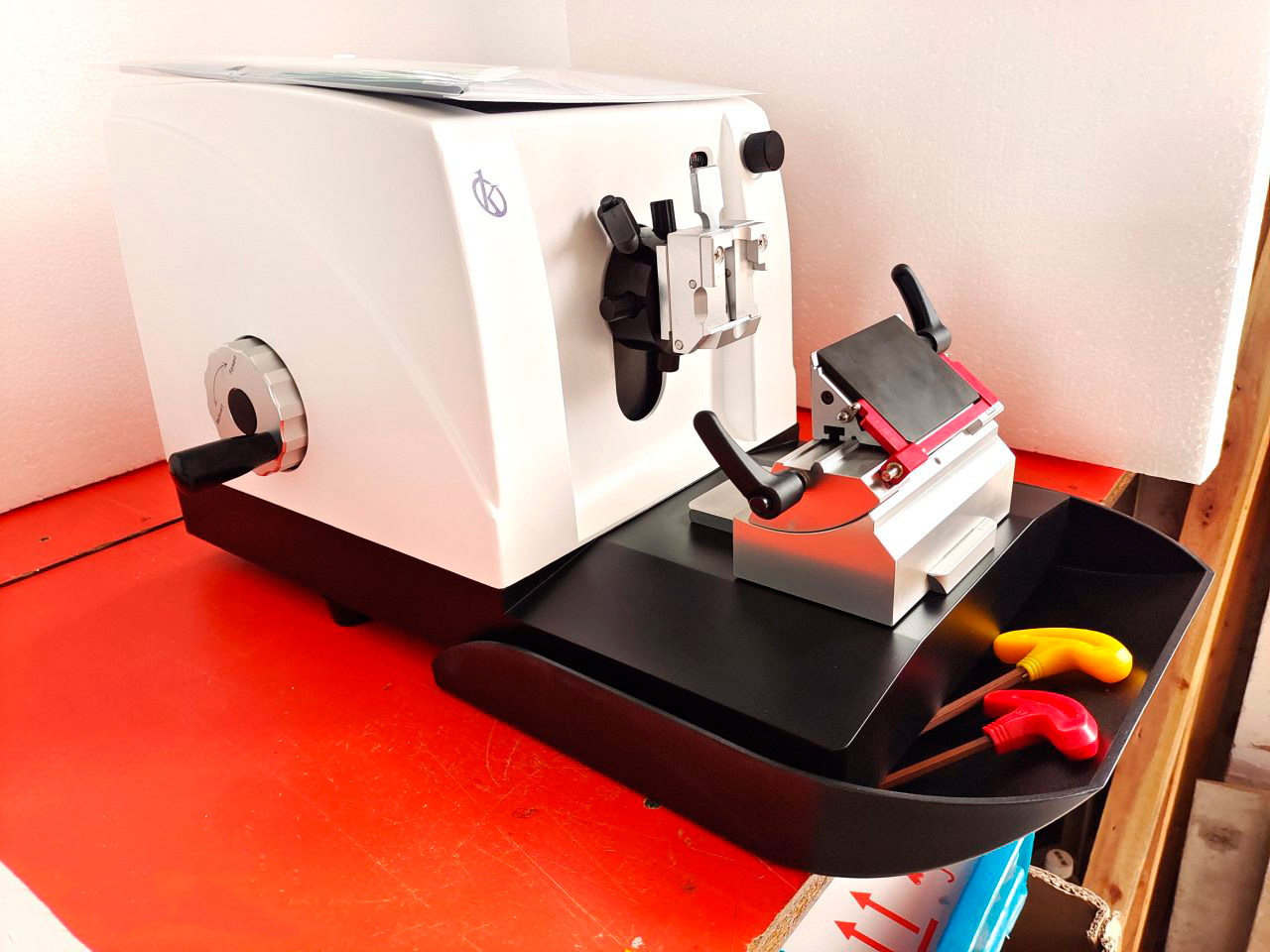

Microtomy is the discipline that deals with obtaining fine serial sections from tissues included in paraffin blocks for their subsequent study under optical and / or electronic microscopy, which makes it one of the basic pillars of procedural techniques of Pathological anatomy.
What is a water purifier?

A water purifier is an equipment or device that removes (eliminates) the impurities present in the water, consider that, for the most part, this dirt is invisible to the human eye. In other words, we can say that water purifiers aim to eliminate impurities and organic and inorganic elements such as germs, bacteria and metals.
What Biosecurity cabinet choose to work with COVID-19?

The biological safety cabinet represents a primary containment barrier that allows working safely with biological agents such as the virus that causes COVID-19. It is equipment designed to prevent the escape of bioaerosols from the work area and, therefore, protects people and the environment from possible exposure to these agents. There are three types, known as: class I, class II and class III.
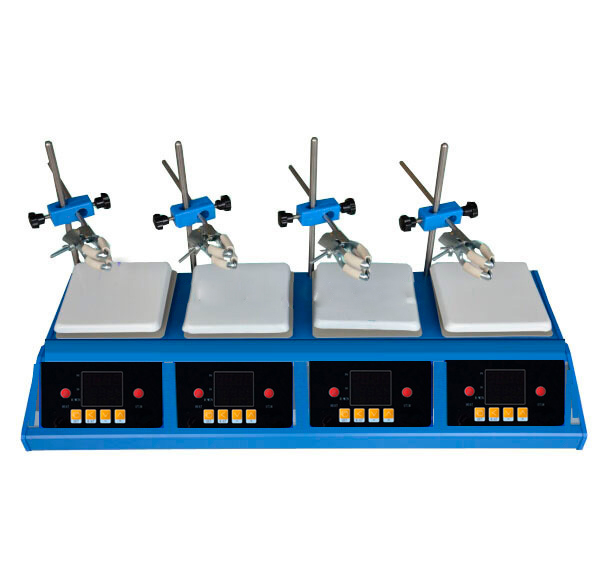
Types of laboratory shakers

Laboratory shakers, also known as mixers, are laboratory products used in the chemistry and biology sectors to mix liquids and prepare solutions and suspensions. These equipments create a movement between liquids or between liquids and solids in order to achieve processes of mixing, suspension, dispersion, homogenization, heat transfer, etc. At present, stirring systems (agitators) are used in all laboratories, be they chemistry, biology, among others.
What is a laboratory magnetic stirrer?

It is an electronic instrument that uses a magnetic field to mix one or more solutes with a solvent in an automated way. This equipment has the ability to heat chemical solutions, it also minimizes the risk of a solution being altered, since generally when the solutions are stirred manually they tend to become contaminated.
How to remove fungi from our microscopes?
Microscopes are essential equipment in any laboratory, some are very simple while others are more complex equipment; however, they are all made up of many parts that require proper maintenance, since they represent a large investment.
The steam autoclave
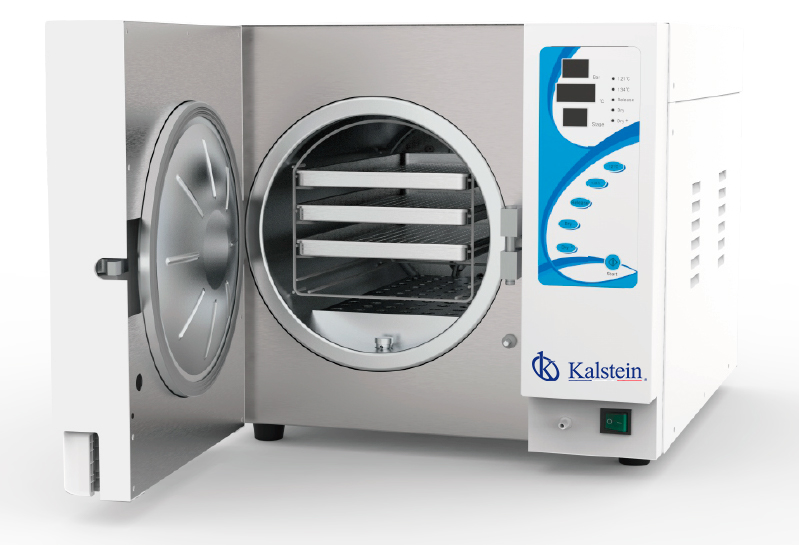

Steam sterilization is the preferred method of sterilization and works by denaturing proteins. Steam autoclaves are equipment designed to use high pressure and temperature steam to kill microorganisms. Sterilization involves the complete destruction of all microorganisms, including resistant bacteria, bacterial spores, protozoa, prions, viruses and fungi present in liquids, surfaces of materials, drugs or culture media.
Double door autoclave: Application
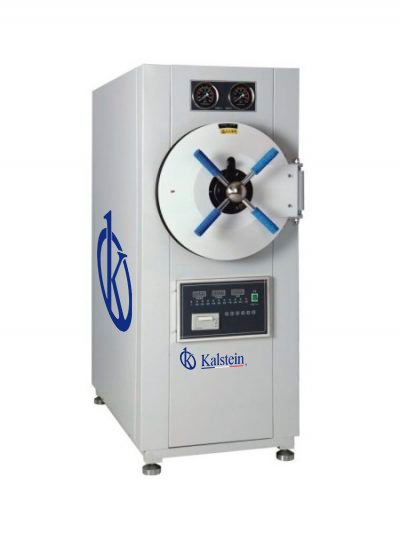

Double door autoclaves are a special type of autoclave used in clean rooms and containment suites. In the case of a clean room application, the autoclave is used for the sterilization of equipment entering a clean or aseptic area, such as a pharmaceutical production environment.
The microtome and bone cutting
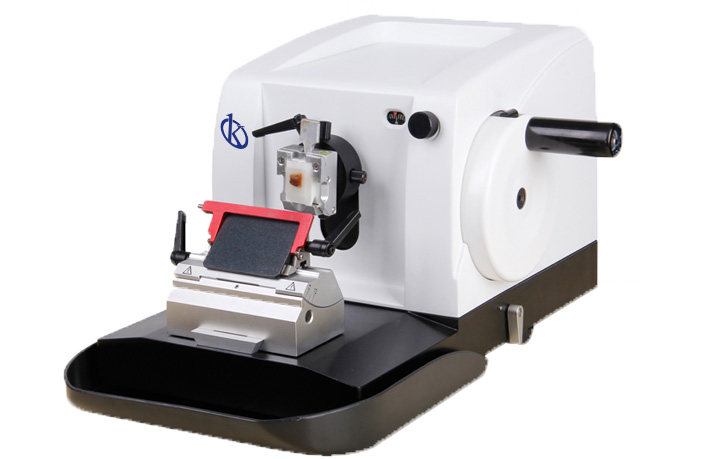

The microtome is a mechanical instrument used to cut biological samples into very thin segments for microscopic examination. Biological samples can be embedded and presented in many ways for sectioning. But more often, these samples are embedded in paraffin wax blocks and the most common way to section these samples is by microtome.
Types of Laboratory Ovens
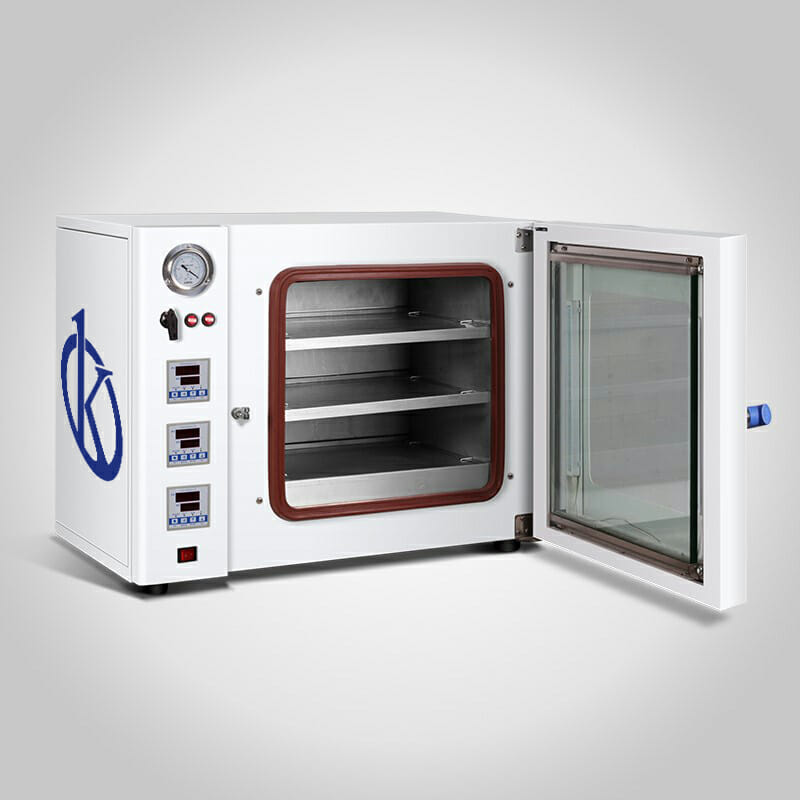

The laboratory ovens or drying oven is equipment used to dry and sterilize glass and metal containers in a laboratory. It is also known as a drying oven. They work between room temperature and 350 ° C. In general, these equipments are made of stainless steel, both inside and outside, this provides them with high durability. In addition, they have a microprocessor that makes sure to maintain a uniform temperature and allows it to be set digitally.
