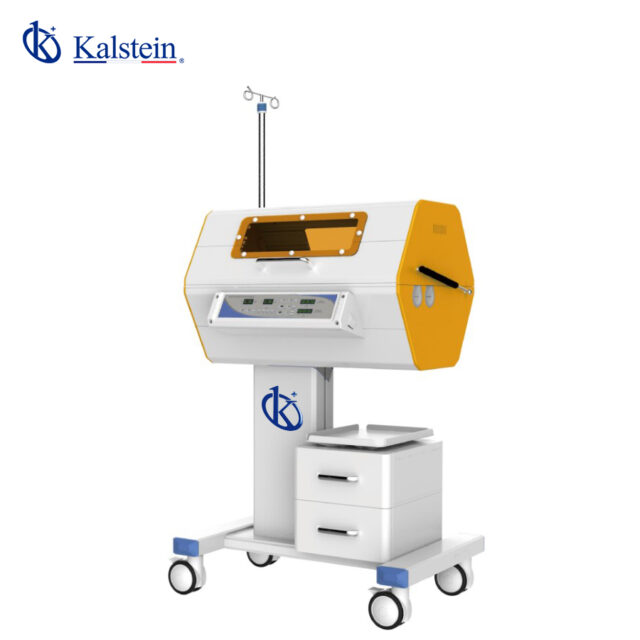
Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit
Introducing our newest addition to the pediatric care equipment line: the Unidad de Fototerapia de Bilirrubina Infantil. Designed to provide the highest standard of treatment for infants with jaundice, this state-of-the-art phototherapy unit offers advanced features to ensure optimal care and speedy recovery. With its adjustable light intensity and uniform illumination, this unit provides targeted therapy while ensuring the comfort and safety of the little patients.
The Unidad de Fototerapia de Bilirrubina Infantil is compact yet powerful, making it ideal for hospitals, pediatric clinics, and neonatal care units. Its user-friendly interface and easy-to-adjust settings make it effortless for healthcare professionals to administer treatment, while its durable construction guarantees long-term reliability. Trust Kalstein for top-quality pediatric care solutions, and provide the best possible care for infants in need of phototherapy treatment.
INFANT BILIRUBIN PHOTOTHERAPY UNIT KALSTEIN
At Kalstein you can find the ideal Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Units for Your Medical Center
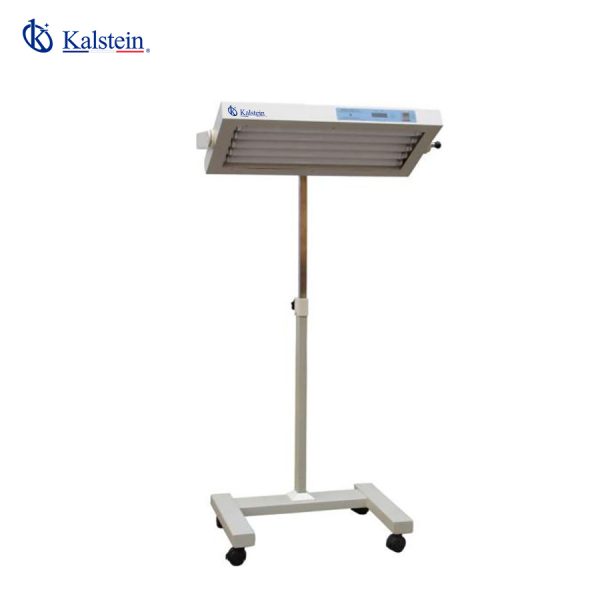

Neonatal LED Phototherapy Unit YR06217
Use blue tube or LED as light source LED Digital Timer, display therapy time & total time Lifting & Mobile Stand, radiant head rotating by angle of 30°/ 60° /9, Use blue tube or LED as light source, Irradiance treatment distance...
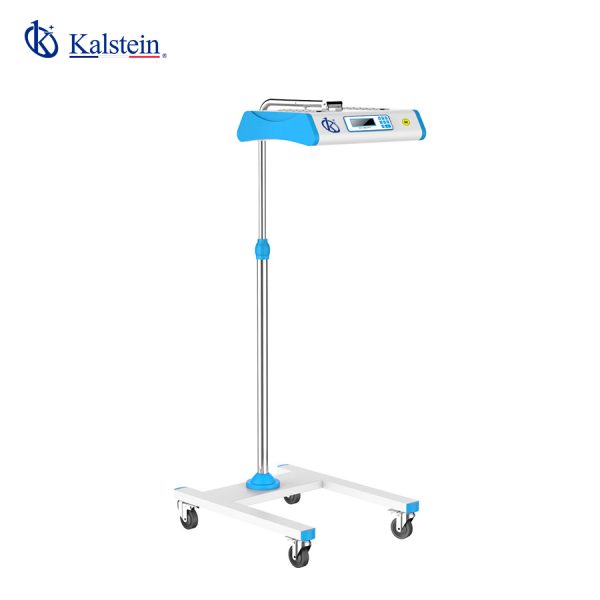
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06220
LCD display indicates the accumulative running time and the current time With white LED lights for easy examination Easy move with wheels Programmable system controller to set different lighting intensity f...
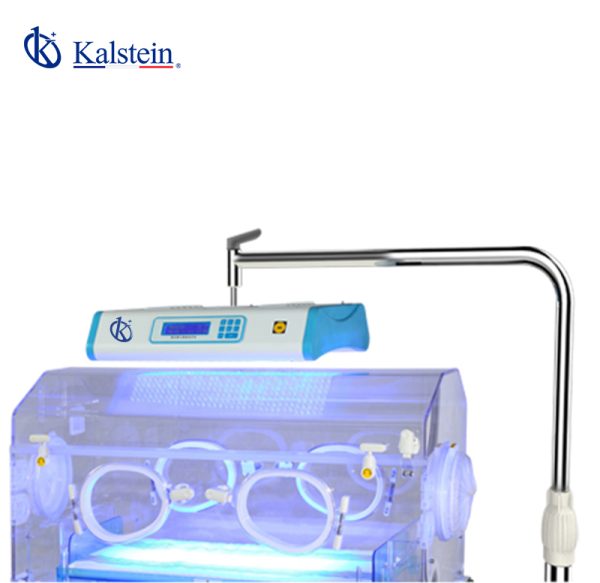
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06221
LCD display indicates the accumulative running time and the current time With white LED lights for easy examination Ceiling type Programmable system controller to set different lighting intensity for differe...
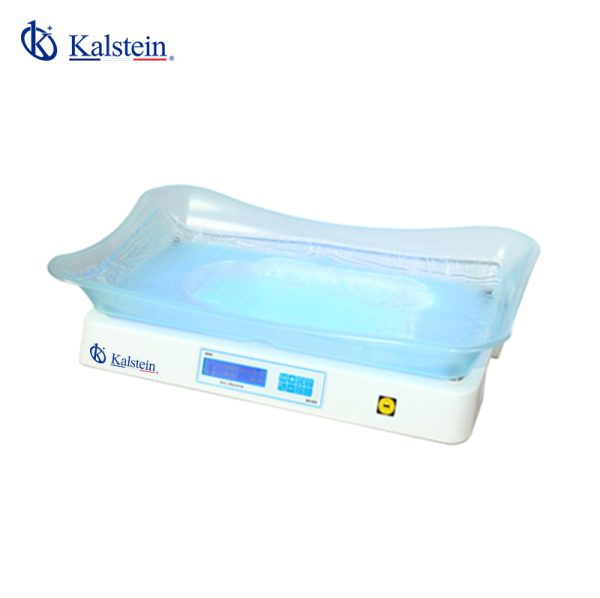
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06222
LCD display shows time information, lighting intensity and skin temperature With white LED lights for easy examination With skin temperature sensor to monitor baby’s skin temperature Internal fan to reduce t...
Our Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit best seller
LCD display indicates the accumulative running time and the current time
With white LED lights for easy examination
Ceiling mount type
Programmable system controller to set different lighting intensity for different time
| Model | YR06218 | |
| Bilirubin radiancy (40cm) | 3750 μ w/cm2(62.5 μ w/cm2/nm) | |
| Bilirubin radiancy (50cm) | 3200 μ w/cm2(53 μ w/cm2/nm) | |
| Lighting intensity | 33%,67%, 100% | |
| White light | Yes | |
| Power | ≤ 60VA | |
| Wave length | 400nm ~ 550nm | |
| Radiant space | 400 × 250mm | |
| Radiant Uniformity | Therapy time set | 0-99h59m |
| Life time | 5000 h |
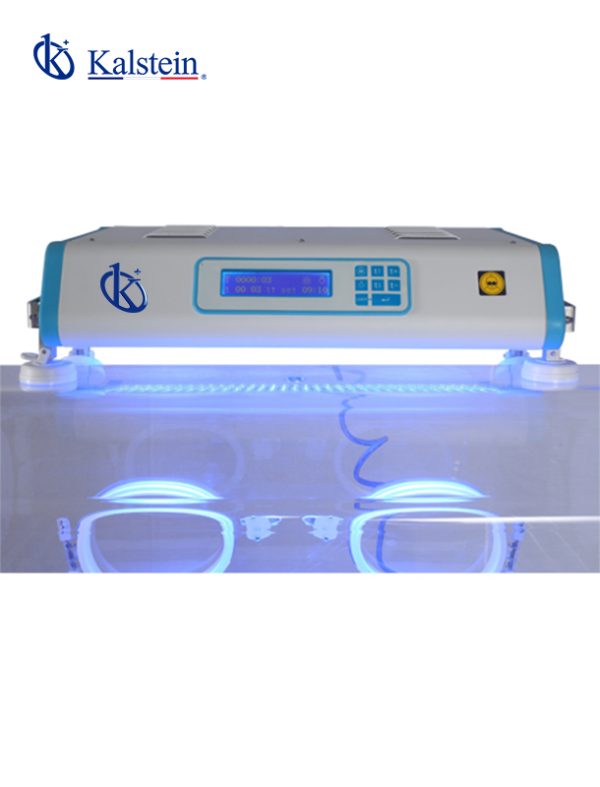

Analysis of the best Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Units for Your Medical Center
When is phototherapy necessary?
Phototherapy is a technique where the effect of light (electromagnetic radiation) is used to treat neonatal jaundice, because light acts on bilirubin, promoting its transformation into water-solub...

What is jaundice? How is it treated?
Jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes caused by the accumulation or deposition of bilirubin. In newborns, the pathological increase in bilirubin is mo...

What are the types of light for childhood phototherapy?
Phototherapy is a therapeutic measure used in specialties of medicine such as pediatrics and neonatology to treat neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. It is a technique bas...

Child phototherapy: can it bring complications?
Although infant phototherapy treatment is the recommended solution when newborns present a severe jaundice, which can be caused by various specific situations, th...
Catalog of models of Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Units on offer
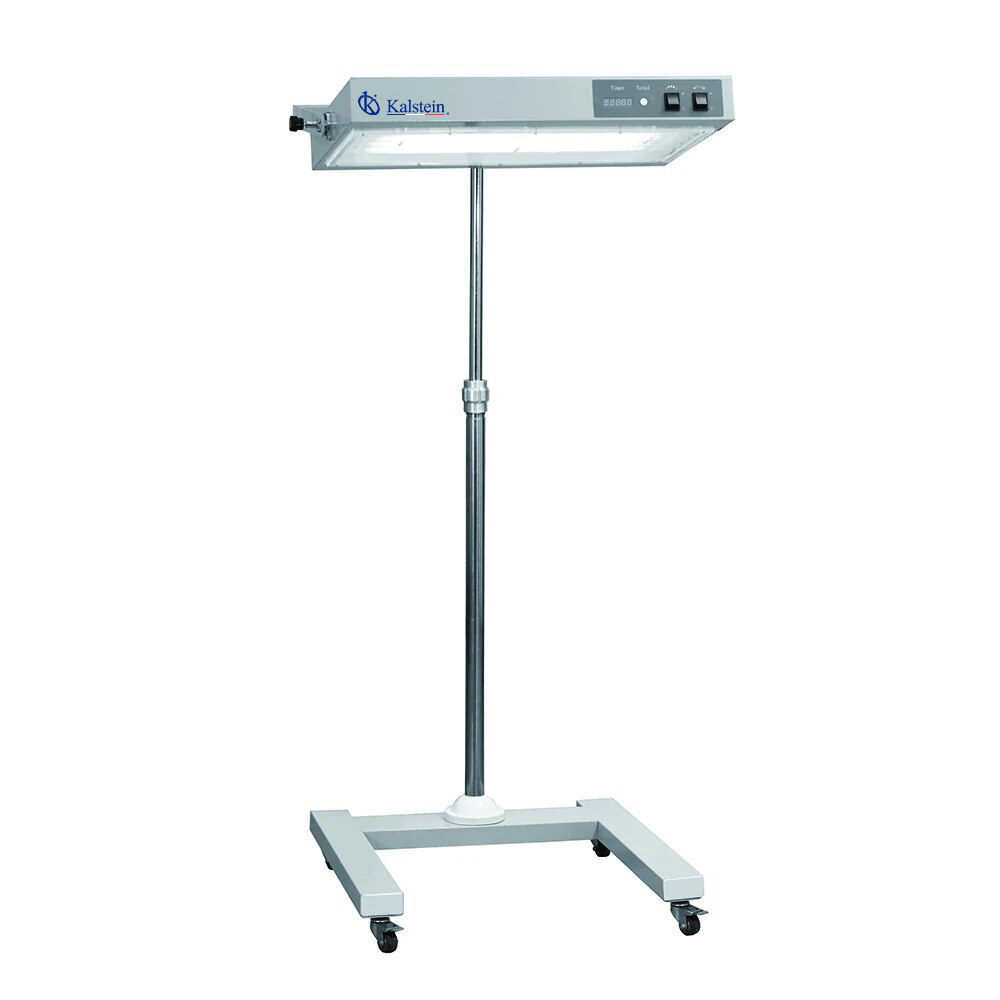
Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit YR02194
Add to cart
Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit YR02195
Add to cart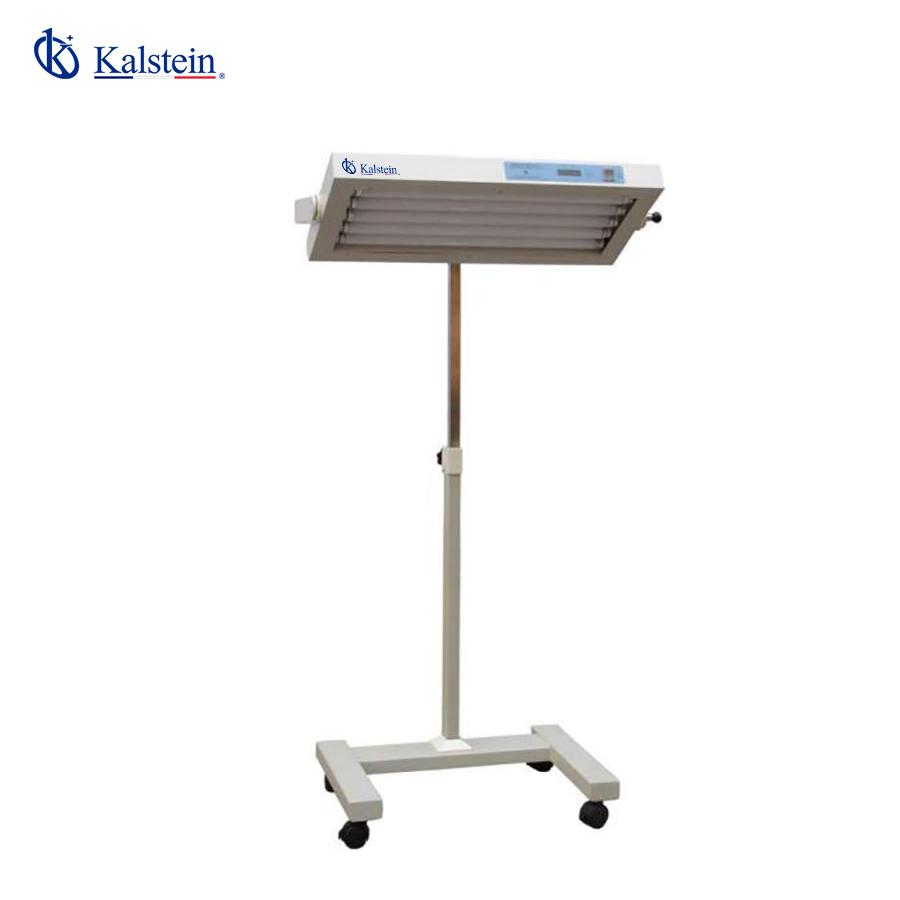
Neonatal LED Phototherapy Unit YR06217
Add to cart
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06218
Add to cart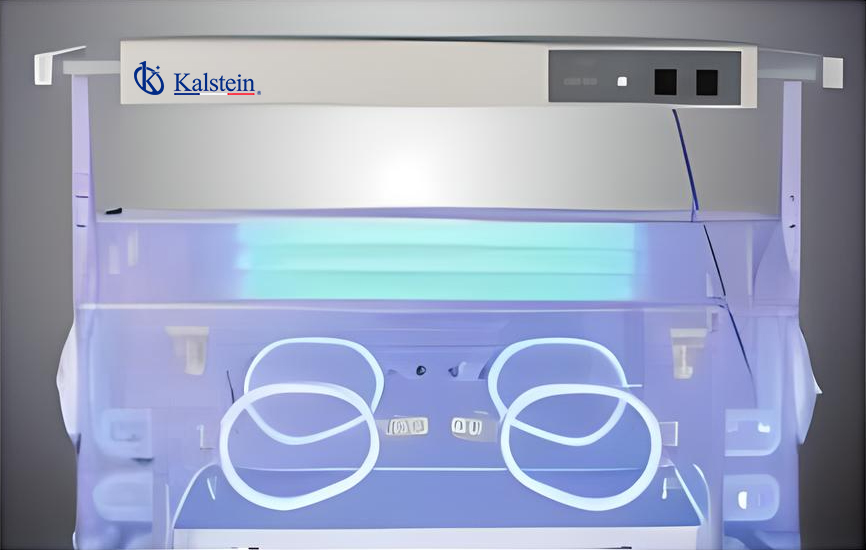
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06219
Add to cart
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06220
Add to cart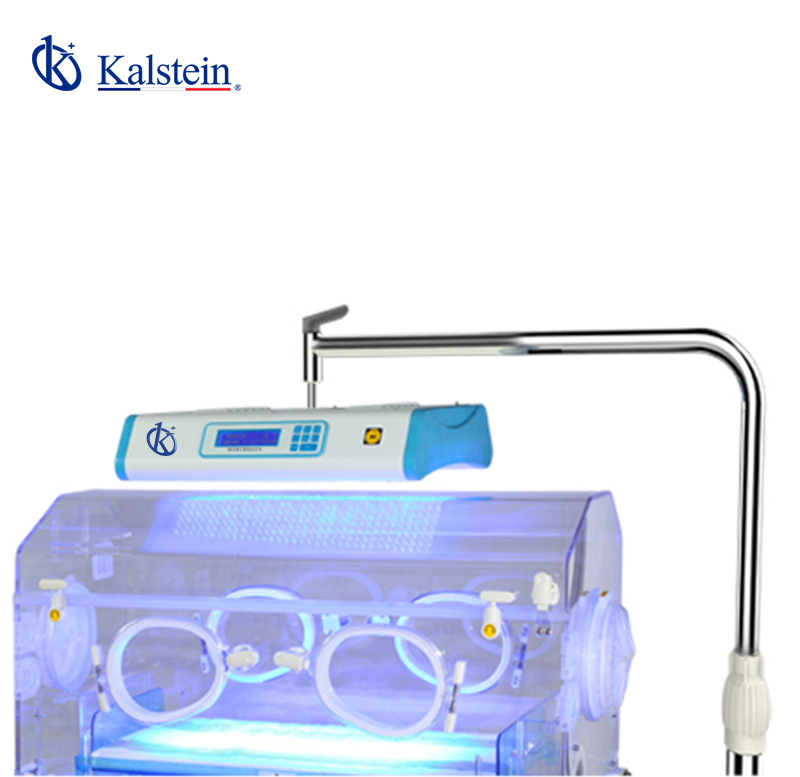
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06221
Add to cart
Infant Phototherapy Unit YR06222
Add to cart
KALSTEIN UPDATED
Guidelines for you to become an expert in Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Units
The Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit equipment are essential products in Your Medical Center, we provide you with guidance and recommendations for a better use, so you can work like an expert.
How long does phototherapy last?
What is the purpose of phototherapy?
How is phototherapy measured?
How effective can a phototherapy unit be for the skin?

Frequently asked questions from our customers about Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Units
To know the price of the infant bilirubin phototherapy units we invite you to send us an email with your request using the contact form. HERE
The delivery time of your Kalstein product will depend on the following:
- Whether the equipment you are interested in is in stock or if it needs to be manufactured.
- The type of freight you have chosen, which can be either air or sea.
- Equipment in stock:
– Delivery Time (Air): 15-30 days.
– Delivery Time (Sea): 45-60 days.
- Equipment not in stock:
– Delivery Time (Air): 30-60 days.
– Delivery Time (Sea): 60-90 days.
You can make your purchase through:
- By email: [email protected]
- By phone: +33 (0) 1 70 39 26 50
- Online shopping: Through the official Kalstein website in your country.
At Kalstein, we provide our customers with inductions and technical support through new online methods. You can visit our induction videos, technical assistance, and guidance provided by a Kalstein team through our Youtube channel (Kalstein English). HERE
Send us a direct message and one of our agents will contact you
Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed dignissim placerat mauris cursus laoreet. Nam feugiat lacus ex, at fermentum sapien accumsan nec. Curabitur auctor porttitor mi non malesuada. Aenean condimentum, purus vitae rhoncus imperdiet, justo eros aliquam ipsum, at egestas leo diam eget libero.

Catalog of models of Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit on offer.
-

Electric Heating Drying Oven YR06446
-

Electric Heating Drying Oven YR05259-2
-

Electric heating drying oven YR05248 // YR05255
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Electric heating drying oven YR05244 // YR05247
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Mini Centrifuge With Large Capacity YR012G
-

Tabletop High Speed Centrifuge YR0137-2 – YR0137-3
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Gel Card Centrifuge YR142-3 – YR142-3-1
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Tabletop High Speed Centrifuge YR019-TG
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Intelligent Electric Wheelchair YR06432
-

Electric Wheelchair YR05445
-

Electric Wheelchair YR05443
-

Electric Wheelchair YR05442
-
Electric Wheelchair YR05444
-

Electric Wheelchair YR05441
-

Electric Wheelchair YR05440
-

Electric Wheelchair YR05439
Descubre más de nuestro catálogo
Tipos de Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit

[Producto] A
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

[Producto] B
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Find out more about Infant Bilirubin Phototherapy Unit with our guides.
Ultrasound Scanner: Real-Time Imaging Diagnosis for Reliable Results
The ultrasound scanner is a fundamental tool in the field of medical diagnostics. This device not only allows for the...
Dental Units: Complete Stations for Modern Dental Care
Dental units have revolutionized how dentists perform their procedures. Over the years, technological advancements have transformed these stations into key...
Transilluminator: Essential Technology for DNA and RNA Detection in Laboratories
The analysis of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, is a critical task in any molecular biology laboratory. In...