Application of infusion pumps in the treatment of hypertension
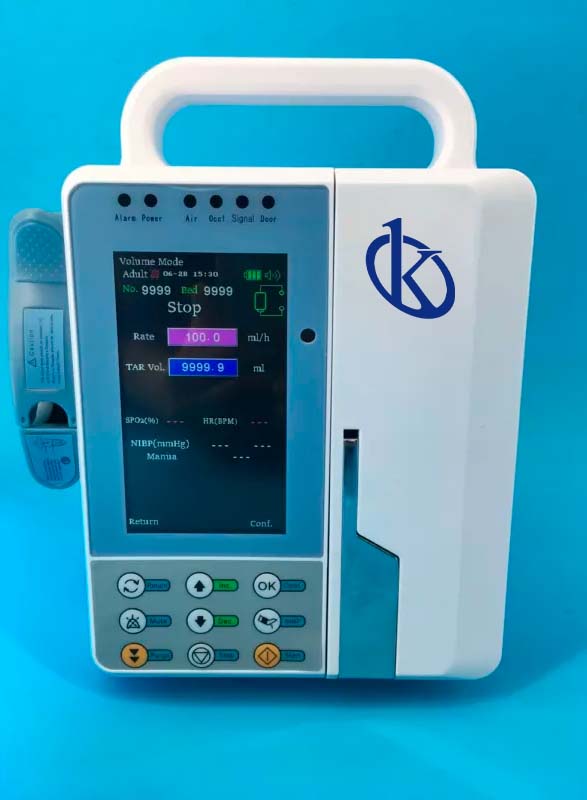
Infusion pumps allow doctors to give drugs in precise doses to treat a variety of conditions, from anxiety disorders and depression to serious diseases such as cancer. The application of infusion pumps as the main treatment of hypertension is becoming increasingly common in the contemporary world.
How should the Radiant Heater be stored for him Baby

The right temperature for a baby is critical to make him comfortable and safe and to avoid possible damage to his delicate skin, many families opt for the use of radiant, safe, efficient and clean heaters by maintaining an ideal temperature for babies at any time.
User interface assessment for an electrocardiograph

The User Interface Assessment of an Electrocardiograph (EKG) is an important process in the manufacture of medical equipment. It takes place before the device reaches the market to ensure the optimal user experience. This means ensuring that users can easily access the information and data they need, as well as that the device is secure, reliable and responsive to user hand movements and preparation.
How to Use an Ultrasound Scanner to Detect Heart Problems
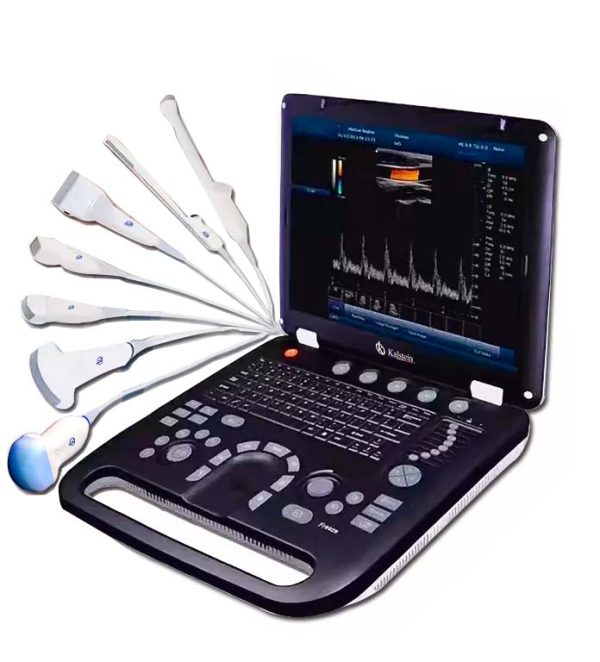
An ultrasound scanner is a useful tool for detecting heart problems; this diagnostic technique is based on sending sound waves through the patient’s heart and then recording the echoes reflected on the screen. The purpose of the scan is to visualize the anatomy of the heart and identify any abnormalities or abnormalities, ultrasound scans are used for many heart disorders.
Ergonomic problems related to the use of the operating table

In the operating room, the ergonomist has as a challenge to ensure the safe and hygienic performance of surgical procedures, minimizing the effort and the risk of injuries in the members of the surgical team. The surgical table, the main element of the operating room after light, is fundamental to comfort and surgical efficiency. The importance of an ergonomically designed surgical table cannot be underestimated.
Evaluation of the efficacy of bilirubin phototherapy equipment

Phototherapy is a treatment of elevated bilirubin in newborns. The main goal of phototherapy is to induce a change in the light in the direct specific bilirubin (excess phototransformation) to make it a more soluble form, allowing bilirubin to leave the body with urine and feces.
Precautions to be followed when using muffles in the laboratory

Muffle is a kind of furnace normally used for melting metals and for cooking materials using thermal energy. The operation of this equipment is based on high temperatures, this is possible thanks to the fact that it is made up of a closed chamber, which is covered with a refractory material that enables a uniform heat delivery inside, being able to reach temperatures of up to 1,700 ° C. On the other hand, The muffle operates in a more controlled way than that of a conventional oven, since it monitors and regulates the temperature at all times.
Patient monitor for monitoring of administered medicinal products
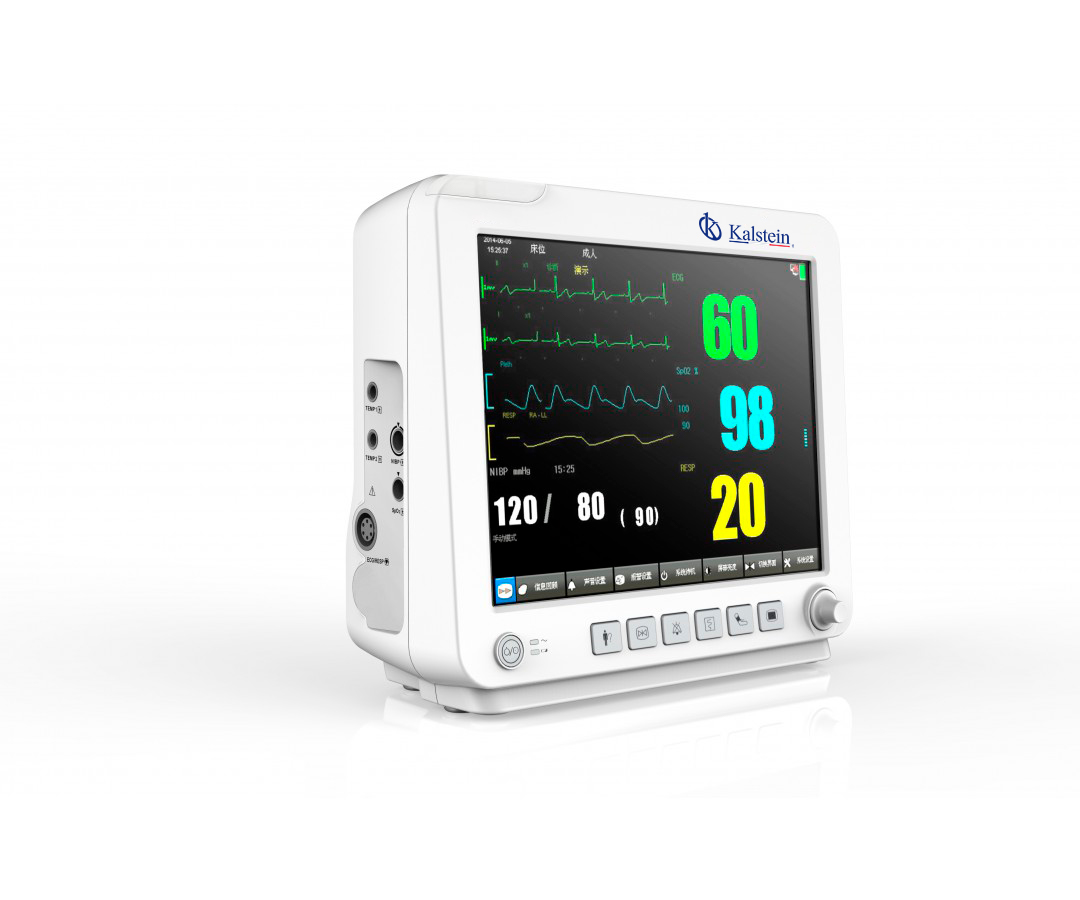
Effective health treatment often requires the use of drugs to control the disease. Adequate follow-up helps improve treatment and health outcomes. This is particularly true for patients with complicated chronic conditions who require close monitoring of their medications such as the treatment of diabetes or a thyroid disorder.
Use and Benefits of Patient Monitors for Proper Care
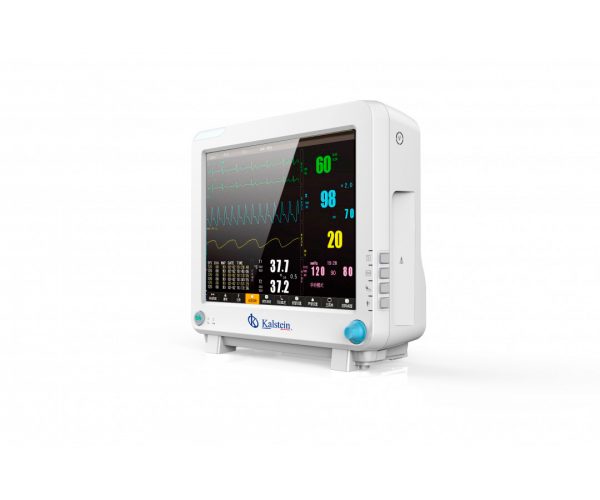
Patient monitors are advanced devices that provide a useful tool for healthcare professionals to examine and treat their patients. These devices can accurately monitor patients’ physical and mental status and also enable monitoring of the condition and recovery.
How Reagents should be handled in the Laboratory ?
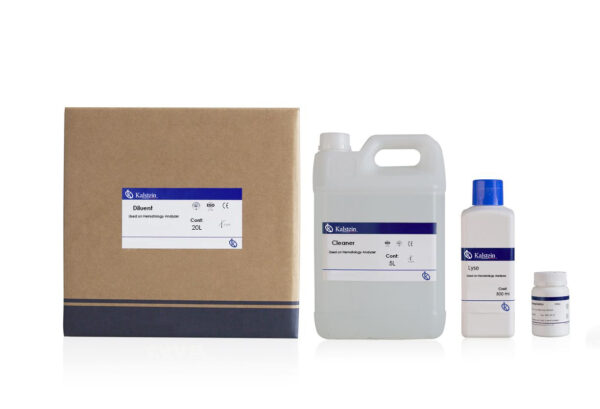

In the laboratory, proper handling of reagents is an essential part of scientists’ work. This is because it is not only about the safety of workers and the environment, but also about the reliable and accurate results of experiments.
